Thursday, December 24, 2009
General Chemistry Notes-4
Saturday, November 28, 2009
General Biology Notes-4
1. Total Number of muscles in human body are 636.
3. Voluntary muscles are striped and are not independent. They are controlled by Spinal cord.
6. Muscles convert chemical energy ( glucose) into mechanical energy. In humans this conversion efficiency is 25%.
7. Muscle fatigue is the accumulation of lactic acid.
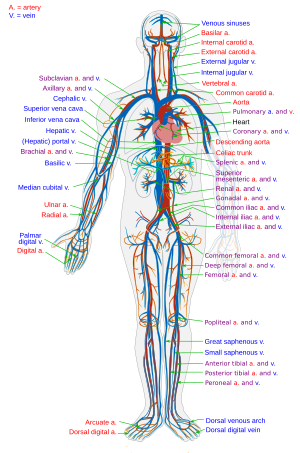
Blood
18. In adult man normally 5.6 liters of blood is formed.
Saturday, November 21, 2009
Geography-4
Priyank Goyal
Thursday, November 19, 2009
Indian History-4
Tuesday, November 17, 2009
Indian Polity-4
Monday, November 16, 2009
Indian National Movement Notes-3
Sunday, November 15, 2009
General Chemistry Notes-3
Saturday, October 3, 2009
Teeth and Bones
Thursday, October 1, 2009
General Relief, Exogenetic Folds and Drainage
Priyank Goyal
Tuesday, September 22, 2009
The Sangam Age and Buddhism
Friday, September 4, 2009
Council of Ministers, Attorney General, Union Legislature, Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha
The Council of Ministers
- Article 74 of the constitution says that there shall be a council of ministers, with the PM at the head, to aid and advise the president, who shall, in the exercise of his functions, act in according with such advice.
- The Word 'cabinet' was not used in the constitution till the 44th Amendment. Found a place in Article 352.
- Collective responsibility: It says that council of ministers is collectively responsible to the house of the people.
- Individual responsibility: Thus ministers are individually responsible to the executive and may be dismissed even if they enjoy the confidence of the legislature.
- Article 78 clearly stipulates that it is the duty of the PM to communicate to the president all decisions of Council of Ministers.
The Attorney General
- First law officer of the Govt. of India
- Qualifications: Same as the Judge of a SC
- Right to audience in all courts.
- Gives advice on legal matters to president
- Not a member of the cabinet
- Has a right to speak in the parliament
- No right to vote in it.
Union Legislature ( Part-V)
According to article 79, the parliament of India consists of the president and the two houses.
Rajya Sabha
- Council of State
- Consists of not more than 250 members
- 12 members are nominated by president
- At Present 245 members
- Only two UT Delhi and Pondicherry is given representation
- Not subject to dissolution
- Terms of individual members is 6 years
- 1/3 of its members retire at expiration of every 2nd year.
- Enjoys equal status with LS except during some special case.
The Lok Sabha
- Max Strength 552
- 530 members chosen by direct elections from state
- 20 members from UT
Two members of Anglo-Indian Community - Nominated by the president
- At present there are 545 members
- Fixed term of five years
- When proclamation of emergency is in force, the term of LS can be extended for a period not exceeding one year at a time and in any case a period of six months after the proclamation has ceased to operate.
- Speaker - Chief officer of Lok Sabha
- President can prorogue the two houses
- The quorum constitute a sitting is one-tenth of the total membership.
Sunday, August 30, 2009
Indian National Movement Notes-2
Saturday, August 15, 2009
Chemistry Notes for Prelims-2
Deliquescence and Efflorescence
* Solids like NaOH and Cacl2 become damp on exposure to moist air. Such substances are called deliquescent substances.
* On the other hand, crystals of washing soda loses a part of water of crystallisation (Na2CO3 . 10 H2O) and crumble into powder. Such substances are called efflorescent substances.
FIRE EXTINGUISHERS
Two methods of extinguishing a fire are:
a. Cutting off the supply of air.
b. Cooling the flames below the ignition temperature.
types:
Ordinary: Mixture of Water and CO2
Foam Type: Fire covered by foam of oil and Sodium Bicarbonate.
Electrical Fires: Heavy Carbon Tetrachloride is put on fire.
COMBUSTION: It is the process of burning accompanied by the liberation of heat and light.
* It may take place in the presence of gases which support combustion eg.Oxygen or Chlorine.
* Farther the substance which burns must be raised to a particular temperature called ignition temperature.
EXPLOSION: It is sudden expansion of gases with a loud noise, owing to release of internal energy.
COMPOSITION OF AIR: Nitrogen: 78%, Oxygen: 21%, Argon: 0.9%
* Air is only a mixture and is not a compound.
* Oil contains unsaturated compounds. They add hydrogen and are converted into solid fats. This hydrogenation of oil is called 'vanaspati'.
Peculiar Properties of Water: Even though molecular weight of water is low, it has unusually high boiling point. It is denser than ice.
Solid CO2 used in refrigerators is called dry ice.
Carbonic Acid is also known as soda water.
A Fuel is a substance that is used to produce heat energy.
Carbon Cycle: During day time , plants take up CO2 from air and return oxygen. At night the plants take in oxygen and gives out CO2. This cycle serves to maintain the % of CO2 in air fairly constant.
Gobar Gas: Obtained by fermentation of cow dung and water, inside a pit in the absence of air, also called 'biogas' used for running cooking, tubewells etc.
Aqua Regia: A mixture of Conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1 is called aqua regia. It can dissolve Gold and Platinum.
Laughing Gas: Nitrous Oxide: When inhaled, produce laughing. Used as anesthetic
Thursday, August 6, 2009
General Biology Notes-2
Plants
Plants are divided into three parts:
1. Autotrophic
2. Heterotrophic
3. Insectivorous
Heterotrophic plants are divided into two parts Parasites- Which are totally dependent on living plants and animals and Saprophytes- Depend on dead and rotting organic remains of plants and animals.
Plants Micro Nutrients
1. N2 : Deficiency leads to decrease in angle between the stem and the leaf.
2. P: leads to abnormal color of leaf
3. Ca: Deficiency : Leaves appear abnormal in form or often show scorching or spotting effect.
4. Fe: Acute deficiency leads to scorching of leaf margins and tips. Mild deficiency leads to mottled patterns on leaf.
5. Mn: Deficiency leads to poorly developed root system.
6. Zn: In citrus plants, its deficiency causes mottled leaves.
7. Boron (B): Its deficiency leads to "Heart rot of suger beet and marigold"
Digestive, Teeth, Skeleton and Muscular System
Digestive System
The canal or body parts in which digestion takes place is called Alimentary Canal. It starts from mouth, and passing through Oesophagus (food pipe), stomach and small intestine finally ends into large intestine. Absorption of digested food mainly takes place in small intestines. Undigested and unabsorbed material then passes down the colon and rectum which absorb the excess water and with the help of putrefying bacteria form faeces. Finally the faeces passes out through the anus.
Human Digestive Enzymes
| Parts | Digestive Juice | Enzyme present |
| Mouth | Saliva | Ptylin |
| Stomach | Gastric Juice | Pepsin+ HCL, Renin, Gastric Lipose |
| Liver | Bile Juice | No Enzyme |
| Pancreas | Pancreatic Juice | Trypsin, Amylase, Pancreatic |
| Small Intestine | Succus Entericus | Peptidases, Invertase, Lipase, Maltase, Lactase |
- Digestion changes proteins into amino acids, carbohydrates into Monosaccharide glucose, fructose into galactose and fats into fatty acids and glycerols.
- Digestion of proteins is initiated in the stomach by the act of the enzyme pepsin.
- More than 50% of the energy content of the common diet comes from carbohydrates.
- For a normal person about 70 g of proteins and about 400-500 gms of carbohydrates are recommended.
Monday, August 3, 2009
Indian Geography-2
Priyank Goyal
Sunday, August 2, 2009
Later Vedic Age
Friday, July 24, 2009
President, Vice President of India
Article (52-151) deals with: Executive, legislature, union judiciary and CAG.
The Union executive in India consists of President, the Vice-President, the council of ministers and the Attorney General of India.
The President
Electroral Procedure: It consists of elected members of the two houses of Parliament and elected members of all the SLA.
Value of vote of an MLA= (Population of the state)/Elected members of SLA X 1000
Value of vote of an MP= No of votes assigned to all MLA/ Total no of elected MPs
Election of president should be done by a secret ballot and based on a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
Art 56: President term is 5 years. His term may terminate either by
-Resignation in writing to VP of India
-By impeachment.
Qualification: -Citizen of India
- 35 years of age
- Be qualified for election as member of LS
- Must not hold any office of profit.
President should not be a member of either house of parliament or a house of any state legislature. Salary 50,000 per month. Pension 3 Lakh/year
Impeachment:
- Either house may start the procedure.
- Can be brought not less than 2/3 of the total membership of the house.
- Also to be passed by at least 2/3 of the members.
Vacancy: - Due to some unnatural cause then
- VP
- Chief- Justice of India
- Senior- Most member of the SC.
The term ‘Executive Power’, actually refers to the power exercised by the council of Ministers in the name of the President.
The Vice President
- Vide Article 63
- Election: By an electoral collage of members of two houses of Parliament
- Qualification: Identical as of president of India except the candidate should be qualified to be a member of the Rajya Sabha.
- Term , Emoluments: 5 years. May terminate by resignation or by removal.
- Gets a salary of 40,000 Rs. Per month
- Functions as Ex-officio chairman of Rajya Sabha ( Article 64)
Wednesday, July 22, 2009
Notes on Indian National Movement-1
Tuesday, July 21, 2009
Notes on General Chemistry-1
CHEMISTRY
SCOPE OF CHEMISTRY:
Deals with matter and the changes that matter undergoes when subjected to the action of heat light, electricity and other matter.
Elements: Substance which cannot be subdivided by any physical or chemical method.
Metals: Silver, Gold, copper sodium etc
Non metals: Oxygen, hydrogen sulphur etc.
Mixtures and compounds :
Iron + Sulphur = Mixture – Possesses both properties of iron and sulphur.
Iron + Sulphur-------------- Heated----FeS--- Compound- Properties of Iron and sulphur are lost.
Kinetic Theory of Matter: It says the pressure of a gas as due to bombardment of the wall of the vessel by the molecules of the gas.
Chemical Reactions:
Decomposition: (AB-------------- A+B)
Combination: (A + B--------------AB)
Double decomposition: (AB + CD----------- AD+ BC)
Displacement: (A +BC---------------- AC + B )
If the heat is evolved in a reaction it is called exothermic if heat is absorbed it is endothermic reaction.
ATOMIC STRUCTURE:
First given by John Dalton : says atom is indestructible.
Nucleas: Rutherford. The entire mass is concentrated in the nucleus which contain protons and neutrons, their total number equal to atomic mass.
The atomic number which is net positive charge on nucleus is equal to the number of protons.
Since the atom is electrically neutral , a number of electrons is equal to the number of the protons revolve around the nucleus.
Chemical Bonding: The force of attraction which binds the atoms in a molecule is called Chemical bonding.
Isotopes: They are atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different atomic masses. They differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Nuclear fission: When certain heavy atoms like Uranium are bombarded with high velocity neutrons, new fast moving neutrons are released along with a large amount of energy. This process is called neuclear fission.
If all the neutrons are used in producing more fission a rapid and violent reaction takes place. This is the basis of the atomic bomb.
Nuclear Fusion: The two isotopes of hydrogen eg. Deutruim and Tririum react to produce, helium, neutron and a flood of energy. This is called fusion, and forms the basis of H-bomb.
Oxidation and Reduction:
Occur side by side.
Wherever there is oxidation, there is reduction.
When Chlorine oxidized Hydrogen sulphide to Sulphur, Hydrogen Sulphide reduces Chlorine to Hydrogen Chloride. Cl2 + H2S--------------- 2HCl + S
Oxidation: Removal of hydrogen or addition of oxygen or removal of electrons.
Reduction: Addition of hydrogen or removal or oxygen or addition of electrons.
Mathces: Side of the Box: Red phosphorous or phosphorous trisulphide.
Match Sticks: Impregnated with borax- so that they can be extinguished without glowing for a long time.
Heavy Water:
Discovered by Urey.
Contains heavy hydrogen atom i.e deuterium(D)
Formula D2O
Density 1.106
Used in Nuclear reactors to absorb neutrons
Saturday, July 18, 2009
Notes on General Biology
The green plants and a few types of bacteria which are completely self supporting are called autotrophs.
This mode of nutrition in green plants is achieved mainly by the process of photosynthesis.
All animals including men and non-green plants show heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
Hetrotrophs obtain all their energy requirements mainly from organic substances like carbohydrates and fats.
FOOD
Energy yielding food: Carbohydrates and fats
Body building food: Protein and Minerals
Protective food: Vitamins and minerals
Carbohydrates:
One Gram of carbohydrate provides 4.1 Cal.
Manufactured by green plants cia photosynthesis.
Lever converts carbohydrates into glycogen and stores in itself and muscles.
Gycogen is known as animal starch as it is not produced in plants.
Excess carbohydrates is converted to fats.
Fats:
One gram of fat provides 9.3 calories of energy.
Stored as future foods.
Proteins
There are made of amino acids which are the only source of nitrogen in the body.
Amino Acids were discovered by William Rash of USA
One gram of protein provides 4.1 calories.
Proteins are raw material for manufacturing of Hormones, enzymes, antibodies etc.
Minerals:
Vitamins and Minerals are called micronutrients while protein, carbohydrates and fats are called macronutrients.
Ca and P form about ¾ of minerals.
Phosphorous: Metabolism
K and Mg: Muscle Contraction
Na and K: Propagation of nerve impulse and for water balance of the body.
Iron: Raw material for RBC
Iodine: thyroid Glands functioning
Mineral Deficiency Diseases
Anemia: Iron deficiency
Rickets : Calcium
Goiter: Deficiency of Iodine.
Water:
An average man contains about 45 litre of water which is 70% of body weight.
Vitamin:
Funk for the first time used the word Vitamin.
Vitamin A, D, E, K:- Fat soluble
Vitamin B and C:- Water soluble
Vitamin (A) (Retinol) :
Sources: Cod lever oil, egg yolk, yellow vegetables.
Deficiency symptoms: Night Blindness, Xerophthalmia.
Vitamin (B) ( Thiamine):
Sources: Grains, meats, green vegetable.
Deficiency symptoms: Beriberi
Vitamin (C) ( Ascorbic acid):
Sources: Citrus fruits.
Deficiency symptoms: Scurvy (Spongy Gums)
Vitamin (D) ( Calcipherol):
Sources: Animal oil and U-V Rays.
Deficiency symptoms: Rickets, Osteomalacia.
Vitamin (E) ( Tocopherol):
Sources: Unpolished grain, animal and vegetable oil and wheat.
Deficiency symptoms: Muscular Paralysis.
Vitamin (K) ( Kgluation or Coagulation):
Sources: Leafy vegetables.
Deficiency symptoms: Improper coagulation of blood,
Lathyrism: Caused by a neurotoxin, found in Kesri Dal
Friday, July 17, 2009
Notes on Indian Geography
Priyank Goyal
Thursday, July 16, 2009
Notes on Early Vedic Age
Wednesday, July 15, 2009
Notes on Indian History: Indus Valley Civilisation
Tuesday, July 14, 2009
Notes on Fundamental Rights
Part III of the Indian Constitution( A 12-35) deals with the FR granted to individuals.
Originally seven groups of rights. But now 44th Amendment ‘Right to property’ deleted.
1) Right to equality and liberty : Art (14-18)
14: Equality before law
15: Prohibition of discrimination
16: Equality of opportunity
17: Abolishes practices of untouchability
18: Prohibits state from confirming any title
2) Right to Freedom. (19-22)
-Freedom of speech and expression
-Freedom of Assembly
-Freedom to form associations
-Freedom to move freely throughout India
-Freedom to reside and settle in any part of the country
-Freedom to practice any profession
3) Right against Exploitation (23-24)
Art 23: Prohibits traffic against human beings and beggar
Art 24: Prohibits employment of children below 14 years of age in factories mines etc.
4) Right of Freedom of Religion (25-28)
5) Right for Culture and Education (Article 29-30)
6) Right to Constitutional Remedies(Article 32)
• Dr Ambedkar call article 32 as “the very soul of the constitution and the very heart of it”.
• In Golaknath case in 1967, the SC ruled that parliament has no power to amend any of the provisions of part III so as to take away or abridge fundamental rights as guaranteed by the constitution.
• In Keshawnand Bharti case, the SC ruled that parliament has power to amend, but it can not destroy the basic structure of the constitution.
• In T.K,Rangarajan Vs Govt of TN and others, SC observed that govt employees including doctors working in state run hospitals and dispensaries have no “fundamental, legal, moral or equitable right to go on strike even for a just cause".
Distinction between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
*Fundamental Rights are justifiable while Directive Principles are not.
* Fundamental Rights are negative and Directive Principles are positive.
* Fundamental Rights responsible for political democracy while Directive Principles are for establishment of economical and welfare state.
* If there is discrepancy between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles then Fundamental Rights will prevail.
The Writs:
Habeas Corpus: “To have a body”- An order calling a person who has detained another to produce the letter before the court to let it know, on what ground he has been confirmed.
Prohibition : It is issued by SC or HC to a inferior court forbidding jurisdiction or to usurp a jurisdiction with which it is not legally vested.
Mandamus: ”We command” : Commands the person to whom it is addressed to perform some public or quasilegal duty which he has refused to perform.
Certiorary: It is issued to a lower court after a case has been decided by it, quashing the decision or order.
Qua-Wananto: It is a proceeding by which the court enquires into the legality of the claim which a party asserts to a public office.
Sunday, July 12, 2009
Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental rights under articles 15, 16, 19
- Some important posts reserved
- right to vote
The Parliament has passed a bill on dual citizenship for persons of Indian Origin ( PIO) living abroad.
Fundamental Duties
--> By 42nd Amendment, part IV A, Aticle 51 A
--> There are 10 fundamental duties.
--> Justice Verma Committee had recommended for enforcement of Fundamental duties by the citizens.
Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP)
-> From Article 37- Article 51
-> Part IV of the Constitution
DPSP as mentioned in other parts of the constitution:
-> Article 350: Providing primary education in mother tongue for people of minority class
-> Article 351: Duty to spread Hindi Language amongst people of India
-> Article 335: To appoint SC, ST in state and union services
DPSP are Affected by Western Liberalism
Some Important DPSPs
Article 44: Uniform Civil Code
Article 45: Free and Compulsory Education for Children
Article 50: Separation of Judiciary from Public Services
Article 51: Development of International peace and Security
Article 49: Protection of National and Historical Monuments

![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=74af4ada-c0c0-41bb-9c6b-c70ee27522b0)


![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=aa076449-0425-40e6-b524-df0fd832b803)
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=6a71076a-70ef-47eb-8a64-a596ec39c451)